
Open Science: Connecting open minds
Open Science is a new approach to scientific research. Its aim is to strengthen collaboration, both between individual researchers and between other parties and scientists. Open Science makes research more transparent, controllable, faster, more efficient, reproducible and more sustainable. The idea is that civil society organisations, patient organisations, companies and other organisations can all benefit from easy access to scientific research. By connecting researchers and their research output with each other we can lay a foundation that stimulates the growth of Open Science, ultimately resulting in a research landscape where all papers are Open Access, data and other resources are shared, and science as a whole progresses.Open Science @ UM
Open Science is changing the world of publishing and scholarly communication fundamentally. New approaches in scientific processes are being explored to open up science and scientific results, and to improve the Findability, Accessibility, Interoperability and Reusability (FAIR) of research data. New ways of distributing knowledge by using digital technologies and new collaborative tools are enabling people inside and outside of academia to benefit from the latest scientific insights. In 2019, Maastricht University approved the policy note “Open Science @ UM“, which paved the way to: 1. Award and remunerate Open Science behaviour2. Stimulate Open Access publishing
3. Make research data optimally suited for reuse
4. Support and facilitate Open Science OSC Maastricht was founded to work on these goals by spreading the word on Open Science, educating our researchers on these practices, and answering your questions.

Rianne Letschert, rector at UM, at the 2019 Open Science event
Our mission
By increasing transparency and enabling access to important knowledge, scientific progress can be improved in both quality and speed, while proving fair and equal access to important sources of scientific data. It encompasses practices such as publishing in open access journals or providing funding to pay for open access fees, encouraging scientists to practice open science by using electronic lab notebooks, and making it easier to publish and communicate peer-reviewed scientific knowledge. While there are exceptions to what can be shared as a result of legal restrictions (e.g. personal patient data and patentable research), most research data are perfect candidates for sharing and provide a rich source of knowledge that has yet to reach its full potential.
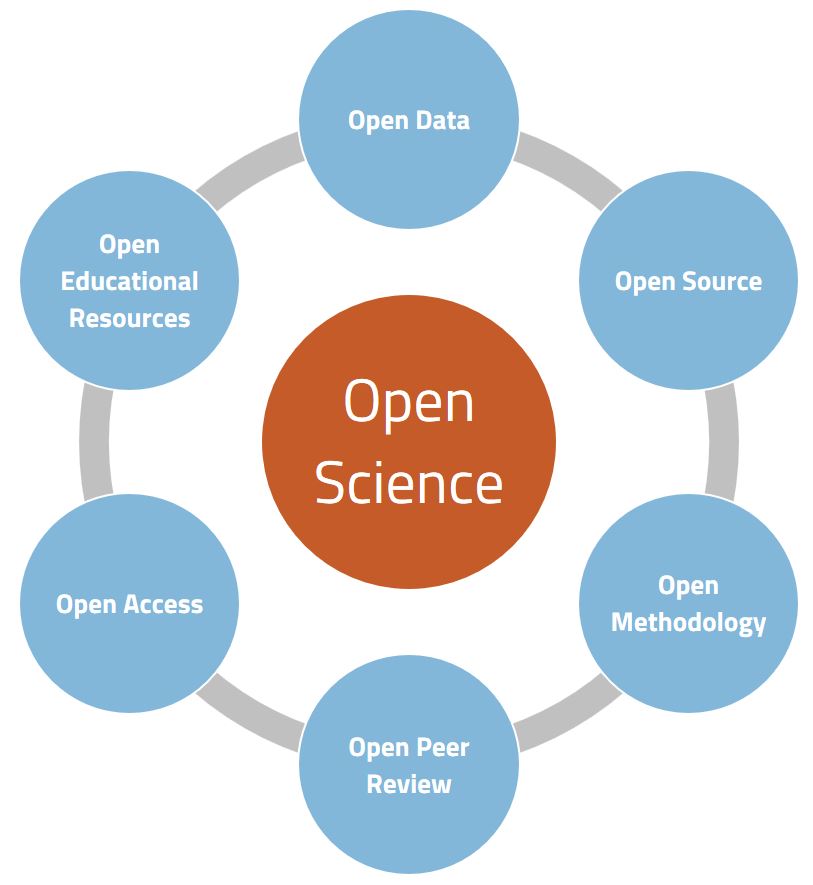
Open Science principles
Maastricht University endorses the principles of Open Science and offers its academics support to put these principles into practice to make science “as open as possible, as closed as necessary”. The Open Science umbrella covers topics such as:- FAIR data use: Whenever possible, research data must be Findable, Accessible, Interoperable and Reusable.
- Open Access: Promoting free online access to scientific information, such as publications and data. In this model, the author pays, not the reader.
- Encouraging the unconditional right to reuse research data, modify them, and reshare them.
- Recognizing and rewarding scientists in a different way: Scientists are usually judged by their publication output and the research grants they have acquired. Open Science also stands for recognition and appreciation of other issues such as educational activities, leadership qualities and social impact.

